Data Integration
Overview
Data integration is actually all about combining information from multiple sources into a single and unified view for the users. Such a process is vital for a company to provide smart decisions as well as efficiency and be at the top game. This article explains what exactly data integration is and why it matters, along with detailed use cases and methods.
The goal of data integration, then, is to give BI users, data analysis, and other applications quick access to accurate information. Data integration enables the connection of all your data sources, which helps empower more informed business decisions—an important factor in today’s competitive environment. Properly executed, data integration cuts IT costs and frees up resources, improves data quality, and ignites innovation—all without systems or data architectures needing massive rework.
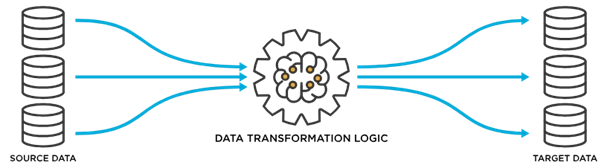
How does data integration work?
There exist various forms of data integration, each presenting its distinct advantages and disadvantages. The optimal approach for your organization hinges on factors such as data requirements, technological infrastructure, performance criteria, and budget constraints.
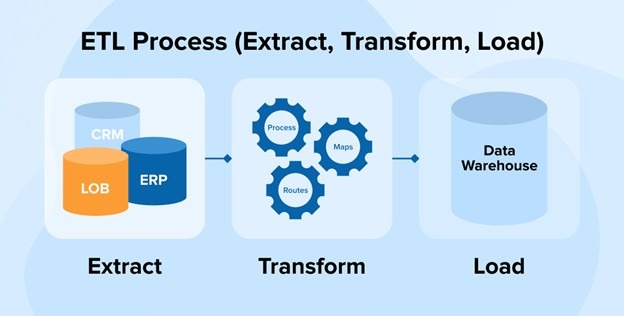
ETL (Extract, Transform and Load)
This is the most commonly used data integration technique.
- Extraction: Data is pulled from the source system into a staging area where it’s cleaned and quality checked.
- Transform: Data is formatted and converted to match the target system.
- Load: The formatted data is then transferred into a data warehouse or another data storage system.
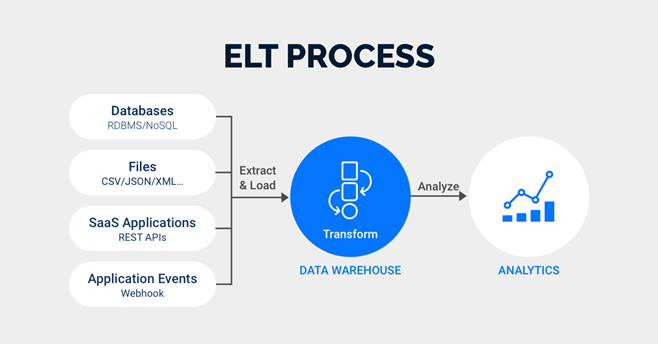
ELT (Extract, Load, Transform)
This method proves to be efficient when both your data source and target reside within the same ecosystem.
-
- Extract: Data is pulled from its source.
- Load: Data is loaded into a database or data warehouse.
- Put together: Data is cleansed, aggregated, or summarized in order to meet business needs.
ELT data pipelines are found to be widely used in big data projects and real-time processing, where speed and scalability are most valued. Preloading the data before transforming it lets ELT fully take advantage of the computational power of such systems. The procedure is much faster than traditional techniques, like ETL, in processing the data and provides greater flexibility in the management of data.
Streaming or Real time Data Integration
It is like a stream of data, not delivered in parcels but flowing constantly, much as a river. This captures and processes data, essentially putting it into the target system in real time. Therefore, its benefits are highly applicable in scenarios where there is an immediate call for insights of real time analytics, fraud detection, and monitoring.
Application Integration
Think about application integration as the ultimate team player for your software applications. It guarantees that data flows effortlessly between various applications, ensuring they all operate in harmony. This becomes particularly advantageous when disparate systems, such as your HR and finance applications, require data sharing and synchronization. It’s fundamentally about keeping everyone aligned!
Use Cases for Data Integration
Every organisations’ needs are different, depending on their industry, products, customers, workflows and other factors. The common factor is that they need data integration for similar purposes. Here are five of the most common data integration use cases that apply across a wide range of industries:
Data Ingestion
Data ingestion can be considered the art of collating information from various sources and moving it to a place for storage, called a data warehouse or perhaps a data lake. This process can be carried out in real-time, like a live stream, or batched. The data is cleaned and standardized so that it is in a ready state for analysis. Migration of your data to the cloud or building a data warehouse, data lake, or data lakehouse are some of the examples.
Syncing records to multiple systems
Many enterprises find that they have multiple independent systems that store the same data. Sometimes this occurs as a result of merger and acquisition activity. For example, if two retailers merge with each other, the two may have many suppliers, partners, and customers in common and have information about all those entities in their respective databases. However, the two brands may run different databases, and the information stored in those databases may not always agree. Enterprises can choose to deal with these situations in many different ways. For example, they may try to combine the databases from the two merged companies, or they may try to move both the finance department and the receiving department onto the same enterprise resource planning (ERP) software in order to eliminate the siloes.
Data Migration
When companies update their IT systems, they often need to move data from legacy systems into newer platforms. Without integration of data, the process of upgrading carries a risk of losing or corrupting such valuable information while transferring. Since the advent of computers, companies have been compelled to exchange data with suppliers and partners. The example of the manufacturer is one scenario where the shipping lists, invoice details, or product information may need to be transferred. Or a hospital might need to receive patient records from independent physicians’ offices and labs
Create Analytics Dashboard
One of the main goals of data integration is to empower businesses with powerful BI tools. By merging data from sources like CRM systems, financial databases, and operational tools, organizations can create detailed reports that drive strategic decisions. Example: A multinational bank integrates its customer transaction data, risk analysis systems, and marketing data. This integration helps them produce reports to assess customer segments, identify high-risk profiles, and plan better marketing campaigns.
Conclusion
Data integration is no longer a choice for business; it has become a need for business survival. It enhances the efficiency of companies, improves their decision-making, and unlocks maximum potential from data. With more and more dependency on data and its exponential growth, managing and integrating data becomes crucial.
For the keen ones eager to know more and the depth of data management, Techcanvass offers Data Analytics Course. This ranges from beginner to advanced levels, providing you hands-on training to master the techniques of data integration so that you can keep up with today’s data challenges.

