Table of Contents
Overview
In this post, we are going to discuss the fundamentals of the Insurance domain. This article will help you in understanding the basics of insurance terms, concepts, and types of insurance. The article will provide you the basic Insurance domain knowledge.
Fundamentals of Insurance Domain
In this article, we are going to discuss the following topics:
- What is Insurance?
- Why is it necessary to purchase insurance?
- How does Insurance work?
- Types of Insurance
- Features of Insurance
What is Insurance?
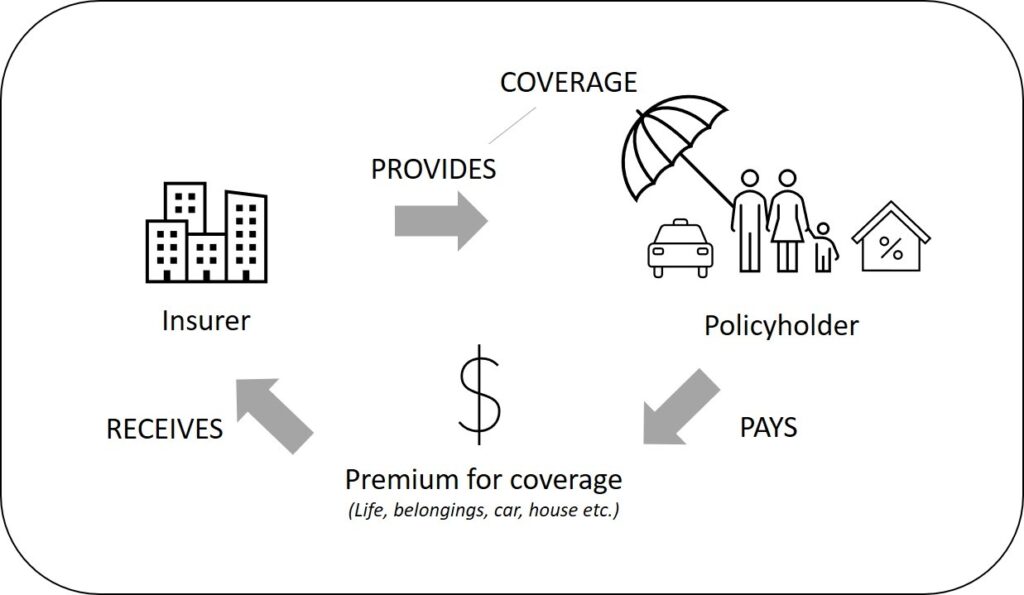
Insurance is a way of managing risks. As individuals, we deal with a lot of uncertainties related to our lives and belongings like houses, cars, etc. Anything can happen anytime causing financial distress. Insurance is a form of risk management where one party (the insured) transfers risks to another party (the insurer) in exchange for a consideration (the premium). The insurance company is said to have provided insurance coverage to the insured.
Useful Links – Insurance Domain Course | BFSI: Banking, Financial Services and Insurance
Why is it necessary to purchase insurance?
Purchasing insurance is an essential part of personal financial management. Just as one would put money in investment vehicles to save, obtaining insurance coverage for unforeseen circumstances is also equally important. It is a way of reducing potential financial losses that arise out of unexpected events such as loss of life, or car accidents. Damage to houses and property, to name a few. So when you are purchasing auto insurance, you can rest assured you will be indemnified for the losses arising in the event an accident arises and your car is damaged. The same goes for life insurance where the designated beneficiaries receive money if the main earner who they are dependent on happens to meet with death. Insurance, therefore, allows individuals and businesses to protect themselves from unforeseen hardships of a financial nature by paying an affordable amount in exchange at regular intervals.
How does Insurance work?
At a high level, insurance is nothing but a pooling of risks. Imagine a community of a hundred individual houses that are insured with a single insurer. Each house owner pays a premium to insure their house. At any given point in time, not all houses will be damaged, so the insurer can pay claims to the ones that are damaged out of the premiums collected, and also operate profitably at the same time after paying all expenses. The chance that the event would occur is a statistical probability that the insurers calculate based on which they determine the premium rates. However, in real life, the way insurers operate is way more complicated. Insurers invest the premium they receive from policyholders to earn returns so that they can pay out claims. They maintain reserves for the purpose and also match their assets and liabilities to maintain optimal balances to run their business.
What can be insured?
For individuals or businesses, insurance is a way of managing risks. Taking insurance is possible only against ‘pure’ risks–ones where there can only be a loss. Speculative risks–where you can gain or lose, are not insurable. For a risk to be insurable, it must be definite, accidental, and big enough to cause hardship to the insured. Further, the interest of the insured must also be insurable–the person must suffer a genuine financial loss if the event for which insurance is obtained occurs. Insurance is a contract between the insured and the insurer. Whenever we take insurance, we get something known as an insurance policy that defines the terms and conditions of the insurance that include, among others, the coverage, features, conditions, and limitations of the policy.
What are the types of Insurance?
Broadly speaking, insurance is of three types: (a) Life Insurance (b) General Insurance, and (c) Health Insurance. Life insurance can be individual life or group life insurance. It also includes annuities whereas general insurance is categorized into personal insurance and commercial insurance. There are further classifications within each category. Health insurance, although a separate group altogether, is sometimes sold by life insurance and general insurance companies. In India, you’ll find many general insurers selling health policies.

Features of Insurance
Whether life or general or health, there are certain features that are common to all insurers. Noted below are a few of them:
- Contract: Insurance is basically a contract between the insured and the insurer where the latter provides a guarantee of financial protection to the former in case of losses arising out of unforeseen events.
- Premium: Consideration is an essential part of any contract along with a valid purpose. In insurance, this consideration is known as premium. Policyholders must pay premiums to receive coverage.
- Agent: A vital of the insurance chain are agents. These are people who are trained and licensed to sell insurance. Nowadays, there are digital channels through which customers can directly purchase coverage from insurance companies.
- Coverage: This is the total amount you are insured for. This is also known as face amount. This is the maximum amount the insurer is liable to pay in the event of loss.
- Policy: This is the contract or the legal document that specifies the terms and conditions under which insurance is sold by the insurer to the policyholder.
- Underwriting: It assesses risks based on which premiums are charged. If the insurers perceive the risk to be higher, they will charge more premiums.
- Claims: It is the process of notifying insurers that the event for which insurance was obtained has occurred. In the case of automobiles, an accident would be a qualifying event for which the car owner would log a claim with the insurance company which will pay the car owner for the loss.
Understanding Insurance Domain Knowledge: A Video Session with an Expert
Conclusion
There is also another class of insurance known as reinsurance. They occupy an important place in the insurance industry and insure insurers. For example, when an insurance company accepts risks, it may not have the ability to pay all its claims how much however cash-rich it may be. That is why they purchase coverage for the risks they have accepted from reinsurers in exchange for premiums. They decide the proportion in which each will bear the losses. So, when a claim occurs, a part of it is paid by the insurer, and another part is paid by the reinsurers.
Insurance companies maintain something known as ‘reserves’ to pay off claims. The world of insurance is big, with many players that include not just the insureds and the insurers, but also other third parties. Also, as compared to a few years back, customers today have more personalized choices to buy insurance that meets their needs. These days, digital technologies are playing a big role in how customers buy insurance and the types of insurance available in the market.
Elevate your insurance career with Techcanvass’s comprehensive Insurance Domain Course! Our program covers underwriting, claims processing, risk management, and industry trends. Benefit from real-world case studies, expert instructors, and stay up-to-date with the latest developments in the insurance sector. Enroll today to master the fundamentals and advance your career in insurance!

FAQs on Insurance Domain
Q1: What is the importance of Insurance Domain Knowledge for my career?
A: Understanding the insurance domain is crucial for professionals, as it allows you to better comprehend business processes, stakeholder requirements, and industry-specific challenges.
Q2: What are the primary types of insurance?
A: The three main types are Life Insurance, Health Insurance, and General Insurance, which protect against different risks.
Q3: How does Life Insurance differ from other types of insurance?
A: Life Insurance provides financial protection for beneficiaries after the policyholder’s death, whereas other types of insurance cover risks related to property or health.
Q4: What should I know about Health Insurance from a professional perspective?
A: Health insurance knowledge is essential for understanding how healthcare costs are managed and how technology is used to process claims and data, which is key for a career in this domain.
Q5: What is covered under General Insurance?
A: General Insurance covers a wide range of non-life risks, including motor, property, travel, and personal accident insurance.
Q6: Is Insurance Domain Knowledge a mandatory skill for a Business Analyst?
A: While not always mandatory, a strong understanding of the insurance domain is a significant advantage that can open up more job opportunities and project roles.
Q7: Can I learn Insurance Domain Knowledge through online courses?
A: Yes, you can. Techcanvass provides a specialized Insurance Domain Training course designed to help IT professionals and business analysts build their domain knowledge and advance their careers.

