Variety in Data
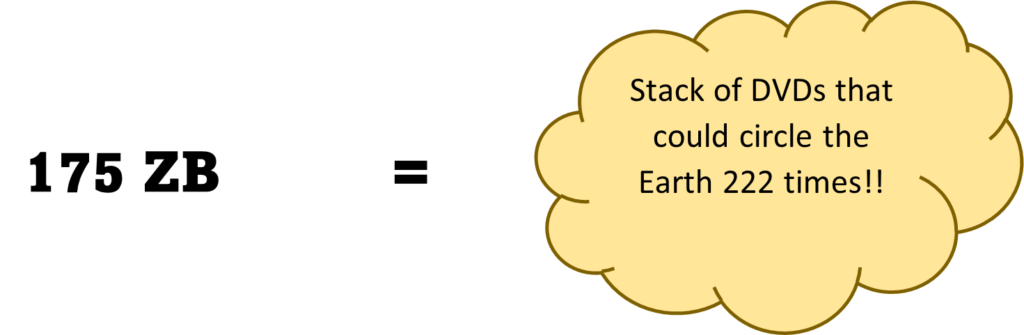
IDC predicts that the global data sphere will grow from 33 Zettabytes (ZB) in 2018 to 175 ZB by 2026! This staggering increase highlights the importance of understanding data types, particularly structured vs. unstructured data. Wow, let us try and imagine this!
Think about the different apps on your smartphone – Uber, Facebook, Instagram, Health, Siri, photos, music playlist, banking, etc. We generate enormous amounts of a variety of data every day. Businesses obtain valuable insights by analyzing various data like pdf documents, customer reviews, audio analysis, webcam video analysis, voice processing, fraud detection, etc. The list can cover pages and pages!
We will explore the different types of data that are generated: structured and unstructured data, along with their unique characteristics and differences. Understanding structured vs. unstructured data is essential, as each type requires distinct methods for storage, processing, and analysis. Structured data is typically organized and easily searchable within databases, while unstructured data, such as text and multimedia, requires more complex approaches for analysis and extraction of insights.
Useful Links – CBDA Training Course | Data Analytics Certification Course | Power BI Course | Power BI: Introduction, Key Features, and Importance
Structured Data
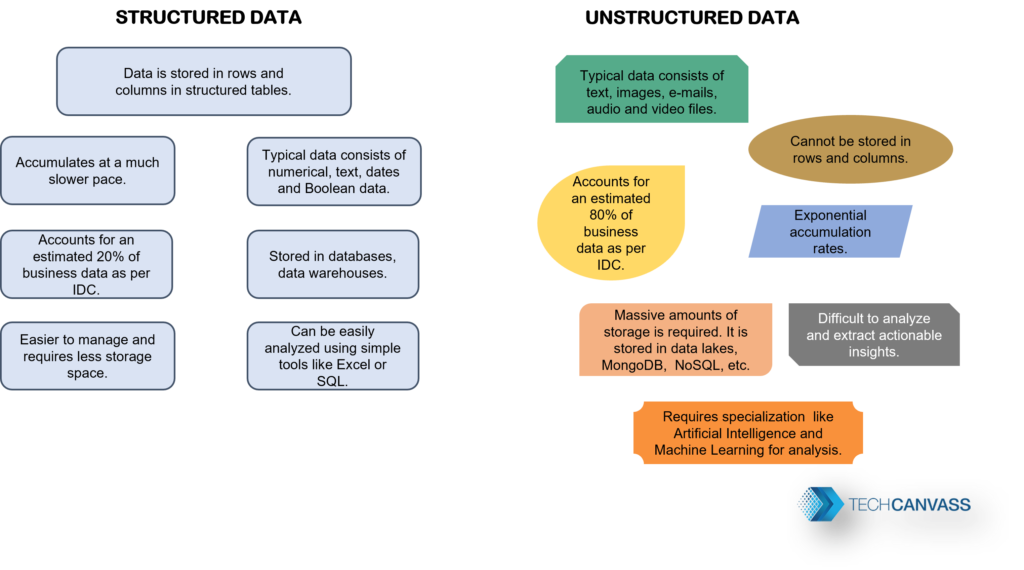
Structured data is highly organized and follows a well-defined model. For example, it fits neatly into rows and columns, similar to data in an Excel sheet, and is typically stored in databases. It can be easily analyzed using SQL (Structured Query Language), allowing users to write queries to analyze the data effectively. Even non-technical users can work with structured data due to its straightforward format. Understanding structured vs. unstructured data helps differentiate the ways each type is stored, managed, and analyzed.
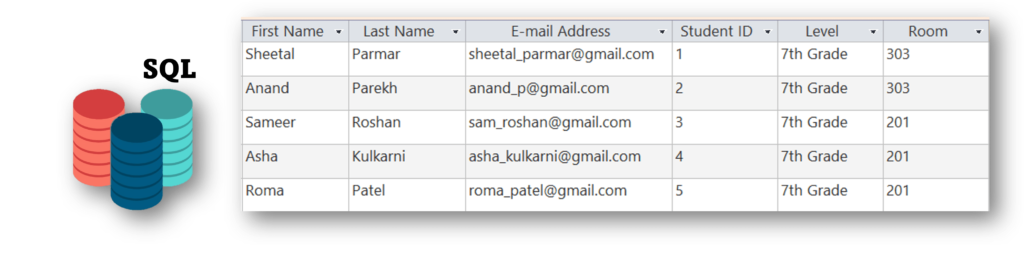
Related tables like customer purchase history, watch history, product information, product inventory, etc., can be grouped in a data warehouse for marketing analysis. Let us explore some examples.
Use Cases
Employee Management: Employee attributes like name, designation, address, salary, the department can be arranged in a structured tabular format. Any changes in these attributes can be easily tracked using SQL queries. Each employee’s data can be efficiently accessed using a unique id.
Inventory Management: For a retail store, keeping accurate track of its current inventory in the warehouse is essential for business operations. As new products are introduced or existing products are modified, these changes need to be promptly updated in the inventory records. This is a classic example of structured data that can be efficiently managed through a database. Understanding structured vs. unstructured data is key here, as inventory data is highly organized and can be analyzed easily, contrasting with unstructured data like customer feedback or images.
Unstructured Data
Unstructured data lacks a definite structure or data model and is stored in its native format. Typical examples include text data, audio, video, social media data, real-time streaming data from IoT devices, and customer reviews, where insights go beyond numbers to capture feelings, opinions, and ideas. For instance, storing customer reviews in a database may not yield meaningful information—especially if the review includes a mix of text, audio, and visuals. This variety and ambiguity make it challenging to fit unstructured data into tables, unlike structured data. Understanding structured vs. unstructured data highlights why unstructured data is managed in specialized databases designed to handle its complexity.
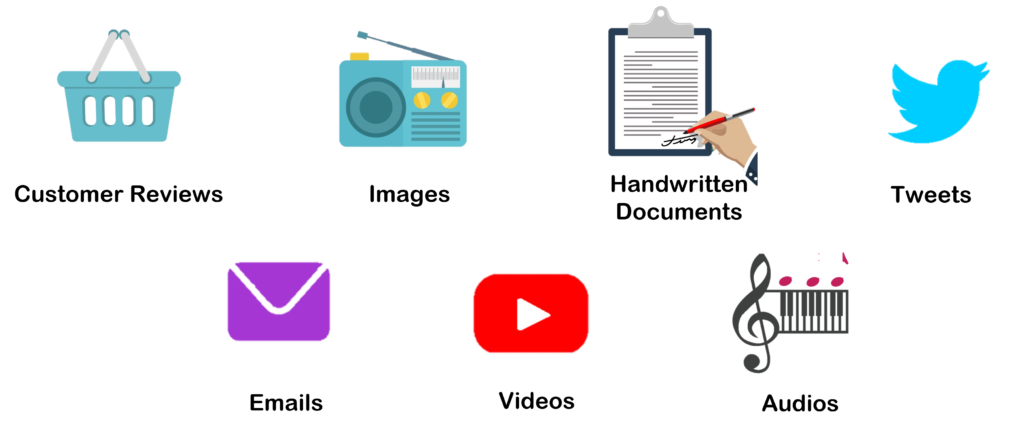

Storing massive volumes of unstructured data is challenging. Handling unstructured data is way more complicated than the structured data. The ambiguity adds to the complexity as there is no pre-defined structure to the data.
Unstructured data is stored in specialized databases like NoSQL, MongoDB, or data lakes. Given the massive scale of unstructured data generation, cloud data lakes, Hadoop, and other systems allow enormous storage and management.
Given the variety of unstructured data formats, it’s not surprising that it accounts for around 80% of the total data generated. Unstructured data holds tremendous insights, and if businesses do not leverage it, they risk missing out on valuable opportunities. According to New Vantage, 97.2% of organizations are investing in big data to tap into these insights. Recognizing the differences in structured vs. unstructured data is essential for organizations aiming to make data-driven decisions and stay competitive in today’s market.
Use Cases
Customer Review Analysis: To find out the sentiment (positive, negative, neutral) from customer reviews requires specialized machine learning algorithms and natural language processing. These algorithms assign a score to each word in a review, and then the overall sentiment is predicted. Expertise is needed to analyze it.
Customer Personalization: Think about the last time you visited your Amazon page. You likely saw sections like “Inspired by your shopping trends,” “Recommended items similar to your past purchases,” and “Inspired by your search history.” Amazon creates a personalized shopping experience for each customer by analyzing their interests and previous purchases. Each customer’s page appears unique due to this personalization. This example illustrates the application of structured vs. unstructured data—structured data like purchase history combines with unstructured data from browsing behaviors to tailor the customer experience effectively.
Did You Know?
Using big data, Netflix saves $1 billion per year on customer retention – Statista
A one-star increase in Yelp rating leads to a 5-9% increase in revenue – Harvard
Key Differences: Structured vs. Unstructured Data
Key Differences
To provide visual clarity, imagine structured data points on the left side, arranged in a fixed-format grid of tiles—organized and uniformly structured. On the right, unstructured data tiles vary in shape, size, and arrangement, lacking a fixed format. This comparison between structured vs. unstructured data highlights how structured data fits into a defined model, while unstructured data resists such formatting, requiring specialized handling to extract meaningful insights.
I am sure you can now confidently identify the differences between structured and unstructured data.
About Techcanvass
Techcanvass is an IT training and consulting organization. We are an IIBA Canada Endorsed education provider (EEP) and offer business analysis certification courses for professionals.
We offer CBDA certification training to help you gain expertise in Business Analytics and work as a Business Analyst in Data Science projects.
You can also learn Data visualization skills by joining our Data Analytics Certification Training and Power BI Certification Course.