When a project is initiated, it comes with several abnormities and risk factors. For a manager handling the project, it becomes essential to understand when and where the project might get affected by external or internal issues. Executing the project without knowing the risks involved is a considerable RISK. Though a 5% chance is that the project gets implemented easily, if not, then the situation might look like a dooming one.
So, every project manager uses certain tools and propaganda to understand the potential risk in advance. The risk register acts as a document that has all the risk management tools to identify and provide solutions for the potential setbacks. The process helps identify, understand and solve the risk before it becomes a major problem.
So, in this blog, we will understand how the risk register works and helps the project manager to evaluate the project’s shortcomings easily.
Read More – What Are Requirement Prioritization Techniques?
What is a Risk Register?
It is basically a log that is created during the early phase of the project. This log captures the unforeseen issues which can appear during the project execution. These unforeseen issues are nothing but Risks. There is no specific format for how to create the log. However, this is a project and an organization specific. If a particular template is used to capture the Risks, let it be followed.
- It is a matrix that can be created in excel or word.
- It is part of the Project Plan.
- It needs to be maintained on regular basis and updated accordingly with the current status.
Learn More – What Is Requirements Analysis and Modelling? | CCBA Certification Training | CBAP Certification Training
Purpose of a Risk Register
As a manager, a Senior Team member, or a Business Analyst, you will be required to understand the RISK REGISTER creation and maintenance. When we start any project, the intention is to successfully complete it. It is a hyperbole ideal situation where one cannot foresee any hurdles during the project execution. These hurdles as RISK help the manager to plan accordingly.
- If these risks are captured in a right manner it will become smooth to meet the project objectives.
- The risk register helps in RISK handling this is also known as risk mitigation. This helps the organization to achieve objectives with fewer slip down along the way.
- It also helps in the preparedness of the contingency plan. It prepares the project and stakeholders for the cases when anv unfavorable situation has occurred. In that case what action needs to be taken without hampering the other work. It ensures that, when undesirable events occur, there are enough strategies in place to minimize and handle the uncertainty.
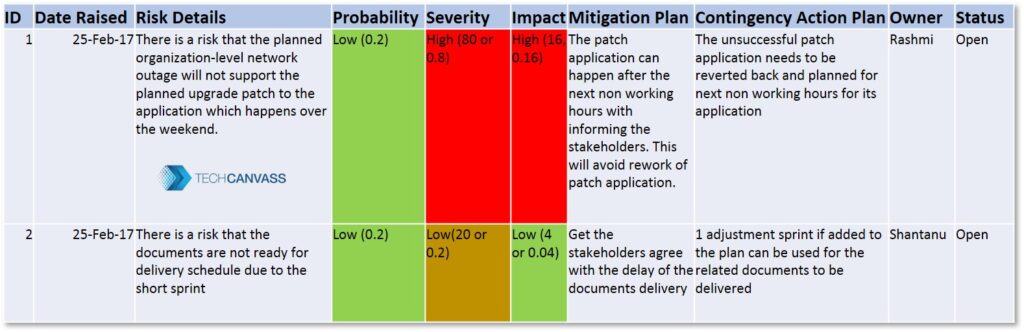
A typical RISK Register looks like this.
How to Create a Risk Register
Creating a risk register is a simple process that involves a lot of research. Let’s look at how a risk register is created in a few simple steps.
- Risk identification
Bring the project team together to discuss potential hazards. Because each team member is in charge of a distinct aspect of the project, tap into their knowledge to assist identify potential project stumbling blocks. You’ll also want to communicate with stakeholders to ensure that you’ve considered their worries and that you’re keeping track of their risks.
- Label the risks
The following step is to describe the project risk. Try to be as detailed as possible while limiting the description to a minimum. It will be difficult to fully appreciate whether a risk has become a serious issue if it is too unclear. For example, if the risk is dependent on the weather, don’t write “The Weather.” Rather, choose a phrase that is directly relevant to your project, such as “India’s monsoon season may cause copper shipping delays.”
- Estimate risk impact
Include everything that the danger can affect so you can come up with a solid approach to deal with it. For example, if layoffs are rumored in your company sector on a regional level, determine the true impact on your project schedule if this occurs.
- Create a plan
This is the time and effort-intensive part of the project risk register, so give it the attention it deserves. You want to be thorough without going overboard. Keep your risk response plan simple and sweet. Do your homework so that if danger arises in the project, you can respond quickly.
Elements of a Risk Register
You have seen various items in the risk register as risk id, date raised, risk details, probability, Severity, Impact, mitigation plan, contingency plans, owner, and status. You can also find the color coding as Red Amber green here. Depending upon the alarming conditions the colors are applied to the register. Red and Amber Green denote the danger alarm as High, Medium, and Low respectively.
Let us understand a few terminologies which are used in a typical RISK Register.
- RISK Id: A unique identifier given to the risk
- Date Raised: When was this RISK identified. This risk can be raised before the project plan is developed or during the execution of the project.
- Risk Details: The details of the risks are captured here. It is advisable to mention what are the consequences in case the RISK occurs.
- Probability: What is the chance that the risk will occur. This can be categorized as Certain, Likely, Possible, Unlikely, or Rare. You can assign it as High – Medium – Low. It is preferred to keep it in percentage like 60% or in value as 0.6, lesser than 1.
- Severity: Severity is the amount of damage or harm a hazard could create. This can be categorized as Critical, Marginal, or Negligible. Every project assigns a value for its severity.
- Impact: This is the value that is arrived as a product of probability and Severity. It shows how important it is to handle this particular risk. To handle any RISK high cost is involved. Cost in terms of money, schedule, resources so on. The project would need approval from the stakeholders. The figure for Impact will help the stakeholders and project manager to plan accordingly.
- Mitigation Plan: to reduce the severity of the RISK, it is advisable to apply some feasible and affordable solutions. For example, let us say the project identified a risk of key team members leaving the ongoing incomplete project. What can the project do beforehand? In this case, one of the mitigation plans could be to assign another person along with the key member to work with him or assist him on the very same work. Risk mitigation needs to be planned, budgeted, staffed, scheduled, and managed like any other important project activity.
- Contingency Action Plan: It is required to come up with a plan which reduces the damage done when the RISK has already occurred. This is called a contingency action plan. In the above scenario where the key team member is planning to leave, the contingency could be to have a detailed KT and a Takeover Plan from the leaving team member.
- Owner: Who is the person responsible to manage the risk. The owner need not be responsible for mitigation action. But he is responsible to get the people together and plan risk mitigation steps.
- Status: RISK Register is a live document. It is a good practice to keep the document updated. The RISK which has already occurred or the RISK which is no more a RISK now should be updated accordingly.
Risk Management Process
The risk management process includes several steps that must be implemented while calculating the risk of a project. The first step involves the identification of the risk within the project. All projects are different, but in many organizations, several projects going on for the year. Looking back at the yearly data, a project manager can potentially identify the common areas that may face risk in the future of the project.
- Collect the project risks: The first step toward the risk management process goes to the collection of the project risks. As mentioned earlier, identification of the risk factors can be done using several data analyses from the previous year’s record.
- Document the project risks: The use of a risk register to document project hazards is critical to project success. It allows you a single location to identify risks, track their history (from when they first appeared to when they were fully resolved), and even assign the risk to the person who identified it and is responsible for its management.
- Resolve the risks: Finally, you can close the project risk once it has been resolved. There’s nothing quite like crossing a danger off your risk record as no longer a project issue. Furthermore, if the risk event has been resolved, you do not want to waste resources on a problem that no longer exists.
People Also Look For – Business Analysis for AGILE Projects
Conclusion
Risk planning and monitoring is an important activity in a project. Project Managers are responsible for overall risk analysis and management, though business analysts are stakeholders in this activity. Risk analysis and management is an important technique in BABOK v3.
We have included risk analysis and management in our CCBA Certification course as well as CBAP certification course.