Table of Contents
Overview
Are you an IT professional or a Business Analyst looking to build a successful career in the fast-growing banking and financial services industry? If yes, then gaining strong banking domain knowledge is the most important first step. The banking industry is a backbone of the global economy, and understanding its fundamentals will not only give you a competitive edge but also open up many exciting career opportunities.
This article is the first part of our three-part series on the banking domain. In this guide, we will cover the core concepts you need to know about the industry. You’ll learn how the banking system works, the key functions of banks, and the journey of the Indian banking system over the years.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear foundation to move confidently to the next parts of the series, where we will dive deeper into retail and corporate banking.
What is a Bank and Banking System?
A Bank is a lawful and regulated financial institution that provides deposit services, keeps the safety of deposits, and allows withdrawals when needed. These services are offered to general public individuals or small businesses to big organizations.
Investor with a surplus can deposit their money with the Bank to earn interest and keep money safe which can be withdrawn when there is a need. Other side, individual or firms looking for funds to fulfill their immediate need and get loans from banks by paying reasonable interest rates. This provides liquidity to money which is a key factor for the economic development of a country.
Banking System
When a group of banks and financial institutions collectively provide financial services to the general public, firms, or a country is termed as a banking system. The banking system provides a common channel for proving and maintaining a payment system, offering lending, accepting deposits, and providing other investment services.
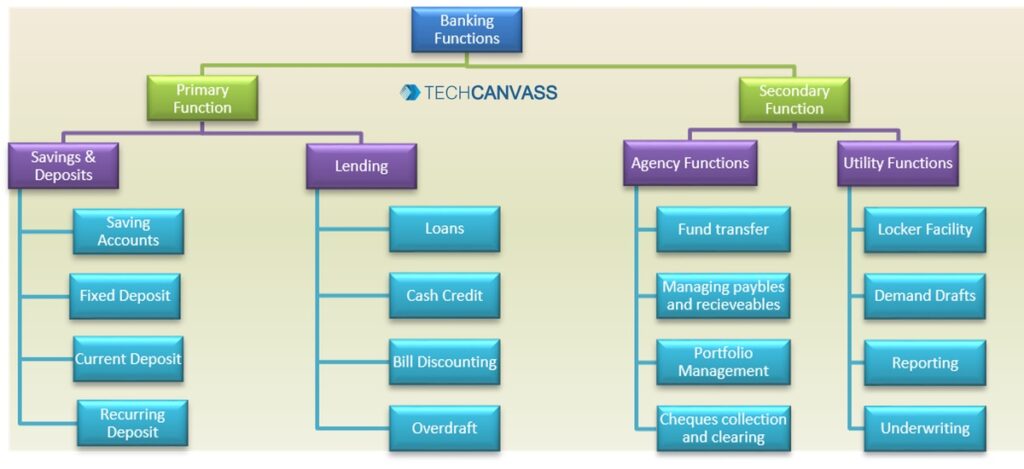
Functions of Banking
Banks play an important role in a Country, its People, and for its Industries to grow. Bank plays a variety of functions and it can be categorized as:
1. Primary Functions – Primary function of the bank is to accept deposits from lenders with surplus and give them to borrowers who need the funds. This maintains the liquidity of money in the market and economy. Banks’ origin was with these 2 primary functions of Deposits and Lending.
- Savings & Deposits – Bank accepts deposits from lenders, safeguards them, pays interest, and allows withdrawing when needed. A variety of products or services are offered in deposits, like savings accounts, current accounts, fixed deposits, and recurring deposit
- Lending – Deposits accepted from borrowers are used to offer loans or other lending services at higher rates of interest which helps borrowers to fulfill their immediate need for managing working capital or expansions. Some of the common examples are loans, cash credit, bill discounting, and overdrafts.
2. Secondary Functions – Commercial banks offer a variety of other services to generate more margins or profits which are also termed as non-banking functions.
- Agency Functions – Bank acts as an agency for its customers and performs functions like fund transfer, managing payables and receivables, portfolio management, and checks collection and clearing
- Utility Functions – Banks also provide a number of utility functions to their customers such as locker facility, demand drafts, reporting, and underwriting
Indian Banking Evolution
The evolution of Banking can be visualizing as for clear understanding:
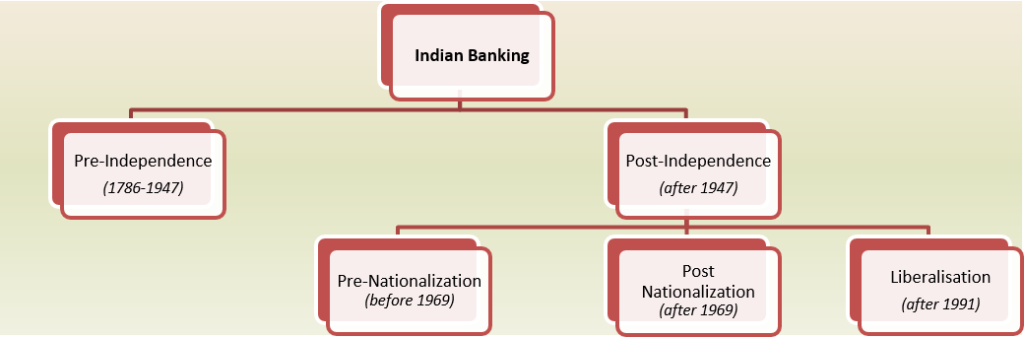
- First bank in India was established in the 18th century with the name ‘Bank of Hindustan” in Calcutta (currently named Kolkata) in 1770 and was the beginning of the Banking system in India
- In 1786, another bank was established as ‘General Bank of India’ but couldn’t sustain longer and failed in 1791
- The oldest and largest bank which is still in existence is the State Bank of India (SBI). It was established as ‘Bank of Calcutta’ in 1806 and then renamed as Bank of Bengal in 1809
- Later on two more banks Bank of Bombay in 1840 and Bank of Madras in 1843 were established
- All these 3 banks were presidential government banks and later on these were merged as ‘Imperial Bank of India’ in 1921
- In the year 1935, the Reserve Bank of India was established on the recommendation of the Hilton Young Commission
- In 1955, after independence ‘Imperial Bank of India’ was changed to State Bank of India
- In 1969, 14 banks were nationalized in order to focus and the development of lagging sectors such as agriculture, small-scale industries, and exports
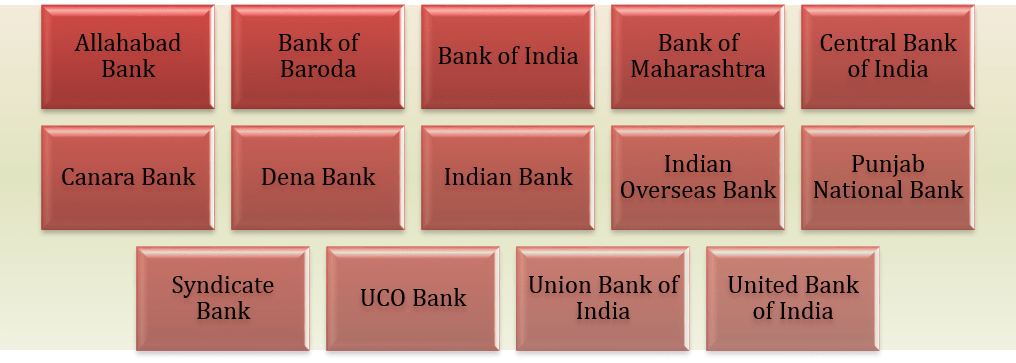
- In 1980, 6 more banks were nationalized

- Specialized development banks were set up to support agriculture. NABARD was established in 1982 and EXIM bank in 1982 for export and import.
- In 1991, foreign and private investors were allowed to invest and ICICI, HDFC, Axis Bank, IndusInd Bank, and a few more banks were given banking licenses by RBI
A Video Walkthrough of Banking Domain Concepts
Conclusion
In conclusion, the banking industry is more than just a world of numbers and transactions; it is a dynamic ecosystem that is essential to the development of economies and the financial security of individuals. As we examine the foundations of this field, we find an intriguing interaction between technology, law, and human ingenuity. Banking is about more than just money; it’s also about innovation, trust, and pursuing one’s financial goals.
Are you ready to find out the truth of the current banking industry? Look no further than Techcanvass’ Banking Domain Training program! Your entry point into comprehending the specifics of the banking industry is this comprehensive training. Our course covers everything, from fundamental ideas to current business trends. Our knowledgeable instructors will walk you through each step, whether you’re a seasoned professional wishing to advance your skills or a novice in the sector. Gain insightful knowledge, advance your professional chances, and become a leader in your field.
FAQs on Banking Domain
Q1. What is the primary role of a bank?
A bank’s primary role is to act as a financial intermediary by accepting deposits from those with a surplus and lending money to those who need it. This core function is vital for maintaining liquidity in the economy.
Q2. What are the main functions of a banking system?
The main functions of a banking system are divided into two categories: primary and secondary. Primary functions include accepting deposits and providing loans. Secondary functions include agency services and other utility services like providing lockers.
Q3. What are a bank’s agency functions?
The Indian banking system’s evolution began with the Bank of Hindustan in 1770. It was shaped by key events like the nationalization of banks in 1969 and 1980, and further liberalized in 1991 to allow foreign and private investment.
Q4. What is the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central bank of India, established in 1935. It plays a crucial role in regulating the country’s banking system and financial institutions.
Q5. What is the difference between a bank and a banking system?
A bank is an individual financial institution, while a banking system is the collective of all banks and financial institutions in a country. The system works together to provide a seamless flow of financial services.
Q6. Where can I get training to learn more about the banking domain?
To gain in-depth knowledge of banking domain fundamentals, you can enroll in a structured training program. Techcanvass provides banking domain training. For more information, please visit our course page Banking Domain Training Course.

